Balancing Robot: Design, Control, and Programming with STM32
Build a self-balancing robot from scratch, mastering STM32 microcontroller programming and robotics topics like PID, LQR, and DC motor control. Get comprehensive guidance on embedded programming, hardware design, and control algorithms.
Enroll Now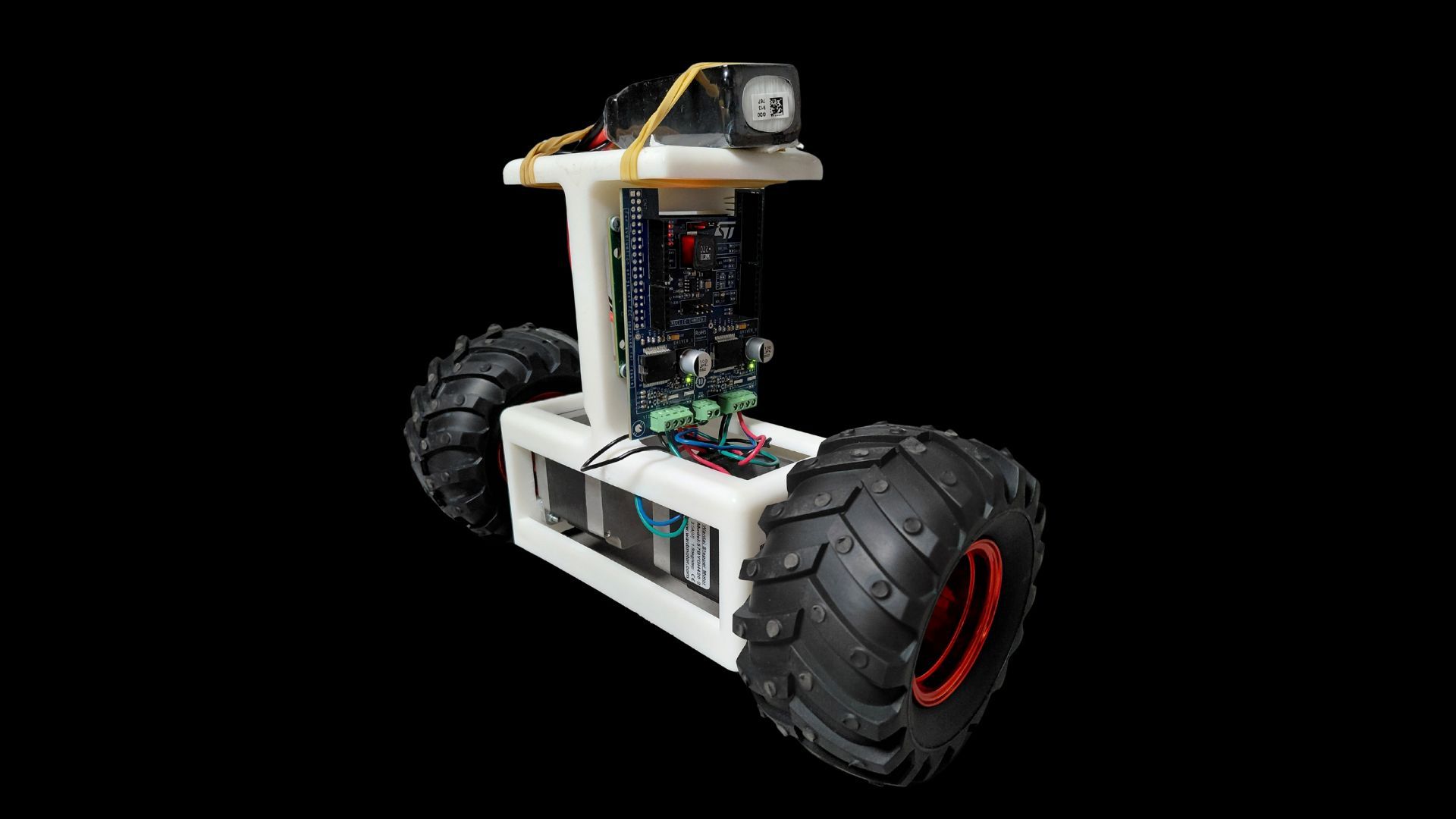
Highly Practical
What you'll learn
✔Managing complex projects
✔ Learning STM32 Debugging tools
✔ Mastering Embedded STM32 Microcontrollers programming (SPI, Timers, PWM, Interrupts, etc.)
✔DC Motor Control: Theory and Implementation
✔ PID Controller: Theory and Implementation
✔ Working with incremental encoders for position/velocity estimation
✔ Using an IMU sensor (gyroscope, accelerometer, and magnetometer) to compute Euler angles
✔ Linear Quadratic Regulator: Theory and Implementation
✔ RC Joystick Integration
Course Content
-
CH0 - Balancing Robot Course Introduction
6 lessons- 1 - Welcome to the course!
- 2 - Slides used in this Course
- 3 - Prerequisites
- 4 - Hardware of the course
- 5 - How to ask questions and other important remarks
- 5 - Source Code
-
CH1 - DC Motor Control
8 lessons- 1 - Motor Control Fundamentals: Part 1
- 2 - Motor Control Fundamentals: Part 2
- 3 - Unveiling the STSPIN240 Motor Driver
- 4 - PWM Signal generation using the Timer of the STM32 MCU
- 5 - PWM Testing
- 6 - STSPIN840 Motor Driver and Custom Hardware
- 7 - Motor Driver Library Integration
- Rate & review this course
-
CH2 - STM32 Timer Encoder Mode
8 lessons- 1 - Incremental encoders theory
- 2 - STM32 Timer Encoder CubeMx Configuration
- 3 - Timer Encoder Mode Test
- 4 - STM32 SWV Configuration
- 5 - Timer Update Interrupt
- 6 - Timer Overflow demo
- 7 - Timer Encoder Library Integration
- 8 - Timer Encoder Library Test
-
CH3 - Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) Controller
5 lessons- 1 - Why do we need PID?
- 2 - PID Explanation
- 3 - PID Library Integration
- 4 - Main File edition for PID Testing
- 5 - Tuning a PID Controller
-
Ch4 - Moving Average Filter
4 lessons- 1 - Moving Average Filter Introduction
- 2 - Library Integration
- 3 - Testing the library
- 4 - Updating the encoder library
-
5 - RC Joystick Integration
6 lessons- 1 - Introduction to the RC Joystick
- 2 - Timers Configuration for capturing input PWM signals
- 3 - Adding the callback function to capture interrupts
- 4 - Testing the RC Joystick
- 5 - Motor Control using the RC Joystick
- Rate & review this course
-
6 - Tilt Angle estimation
37 lesson- Introduction to the Attitude estimation
-
Attitude Estimation Course Excerpt CH1
- 2 - STM32 CubeIde Project creation
- 3 - Using SWV for printf function
- 4 - Using SWV to plot variables
- 5 - SPI theory
- 6 - SPI Configuration using STM32CubeMx
- 7 - SPI wirings
- 8 - Reading ‘Who am I’ register
- 9 - Sending data through SPI
-
Attitude Estimation Course Excerpt CH2
- 1 - First version of the library
- 2 - Testing the library
- 3 - How to read the magnetometer?
- 4 - Magnetometer update 1
- 5 - Magnetometer update 2
- 6 - Testing a new version of the library
- 7 - DMA Theory
- 8 - DMA configuration
-
Attitude Estimation Course Excerpt CH3
- 1 - Removing gyroscope biases
- 2 - Magnetometer bias explanation
- 3 - Timer Update Interrupts
- 4 - Magnetometer bias removal
- 5 - Normalization and scaling of IMU data
- 6 - ARM MATH Library Installation
- 7 - Library Integration
- 8 - A notion of frame
- 9 - Testing the library
-
Attitude Estimation Course Excerpt CH4
- 1 - Attitude estimation, slides
- 2 - A notion of frame in detail
- 3 - 2D rotation
- 4 - Euler angles and Rotation Matrix
- 5 - Using the accelerometer to obtain pitch and Roll angles
- 6 - Using the magnetometer to obtain the Yaw angle
- 7 - Using the gyroscope to obtain the Euler angles
- 8 - Library Integration
- 9 - Complementary Filter
- 10 - Testing the libraries
-
Attitude Estimation, final library integration
- 2 - Tilt angle estimation: Final library integration
-
7 - Linear Quadratic Regulator
7 lessons- 1 - State-Space Design
- 2 - Technical Article Introduction
- 3 - Matlab Script
- 4 - Library Integration and LQR Implementation
- 5 - Testing
- 6 - Sign Explanation
- 7 - Rotation Problem
-
8 - Rotational Drift and Final Joystick Integration
2 lessons- 1 - The rotational drift and how to eliminate it
- 2 - Controlling the robot by joystick
NICE TO MEET YOU
Tutor
Greetings! I'm Yerke, the founder/editor/SEO/ loader/marketer of SteppeSchool. With a Bachelor's degree in Electrical Engineering and a Master's degree in Robotics/Mechatronics, I completed my Ph.D. in Robotics/Mechatronics.
Currently, as an automation engineer, I spend my free time teaching people about electronics, embedded programming, and robotics. For years, I've been curating insightful content on my YouTube channel (+700k views), offering valuable insights to students and enthusiasts alike.

Steppeschool Reviews
Lifetime, Balancing Robot Coding
$80
✔Flexible payment plans
✔Source Code available
✔Lifetime access
✔ 81 lessons
✔ 10 hours of video content
✔ PDF Materials
Flexible Payment Plans
Choose to pay once for lifetime access or spread the cost over several easy monthly payments — all shown at checkout.
Cancelling & 14-day Money-back guarantee
I'm sure you'll enjoy this course! But if it doesn't meet your expectations, no problem—you can get a full refund within 14 days and cancel anytime, no questions asked.
Target audience
Built For Engineers Like You
➜ Who wants to understand how robots are generally made
➜ Who wants to implement control systems algorithms in the real world
➜ Embedded developers ready to dive deep into flight controller firmware using STM32.
➜ Robotics enthusiasts who love experimenting with sensors, PID control, and motor drivers.
➜ Makers who want to build a robot that works *because of their own code*, not prebuilt libraries.
➜ Researchers or educators exploring control systems and UAV dynamics in practice.
Requirments
WHAT you'll need
✔ Hardware for the balancing robot: frame, motors, wheels, etc. (we will discuss in the course)
✔ STM32 MCU
✔ Basic knowledge of programming STM32 MCUs
✔ Motivation


